As a proponent of long-term thinking in your company, you’ve likely encountered resistance. You may feel isolated, struggling to articulate the value of strategic foresight to colleagues focused on immediate concerns. This guide aims to provide you with a framework to effectively communicate the importance of long-term strategic planning (LTSP) and engage others in this crucial mindset.
The Challenge of Long-Term Thinking
You’ve probably experienced this scenario: In a meeting, you highlight a future your colleagues can’t see. The potential long-term consequences seem obvious to you. Unfortunately, your team, preoccupied with urgent problems, lacks the energy to consider your strategic viewpoint. They opt for the quick satisfaction of immediate resolutions.
Afterwards, you realize that fundamental issues remain unaddressed. It feels like you’re only discussing surface-level solutions without questioning the underlying approach.
If this resonates with you, you’re not alone. Many forward-thinking professionals struggle to convey the importance of LTSP. But there’s a way to bridge this gap and bring others into long-term thinking: the Three Horizons Framework by Curry, Hodgson and Sharpe.
Horizon 1: Understanding the Decay of Current Offerings
Every organization provides value through its products or services. However, it’s crucial to recognize that these offerings have a limited lifespan. Each day brings you closer to the point where your current solutions become obsolete.
Consider the photography industry. Until the 2000s, companies like Kodak and Fuji thrived selling film. Today, the average consumer has no interest in this product.
This decay in demand is a universal truth in business, illustrated by the following curve:
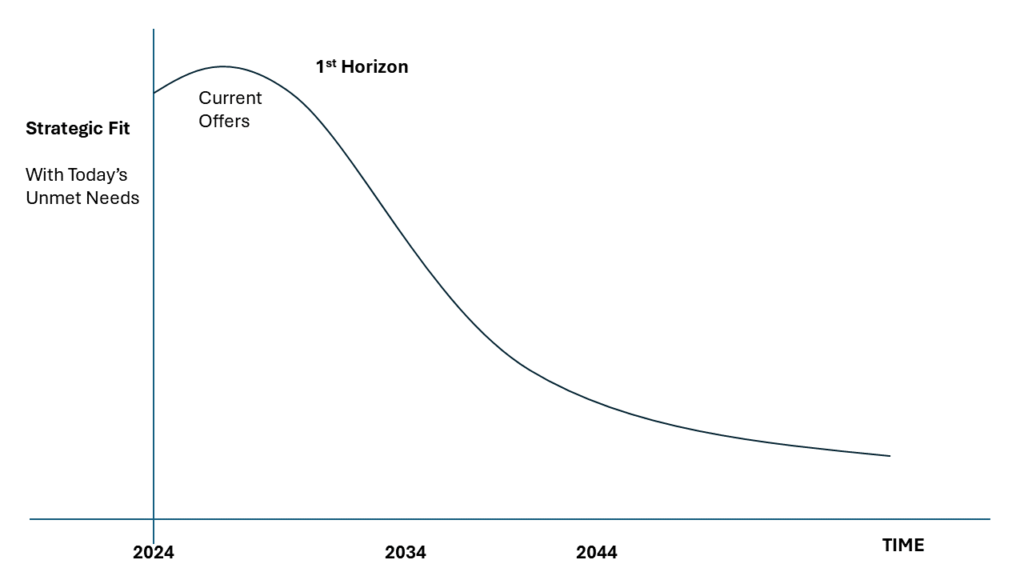
The key question is: How long will your current strategic fit last?
As an LTSP advocate, you’ve likely considered this. Now, you have a visual representation to share with your colleagues, helping them grasp this concept more easily.
Horizon 3: Recognizing Future Opportunities
While managing current operations is crucial, it’s equally important to look for signs of future trends. These “faint signals” can be found in emerging technologies, evolving customer needs, new regulations, environmental changes, and various other areas.
By paying attention to these signals, your team can craft narratives about potential futures. This foresight defines the third horizon:
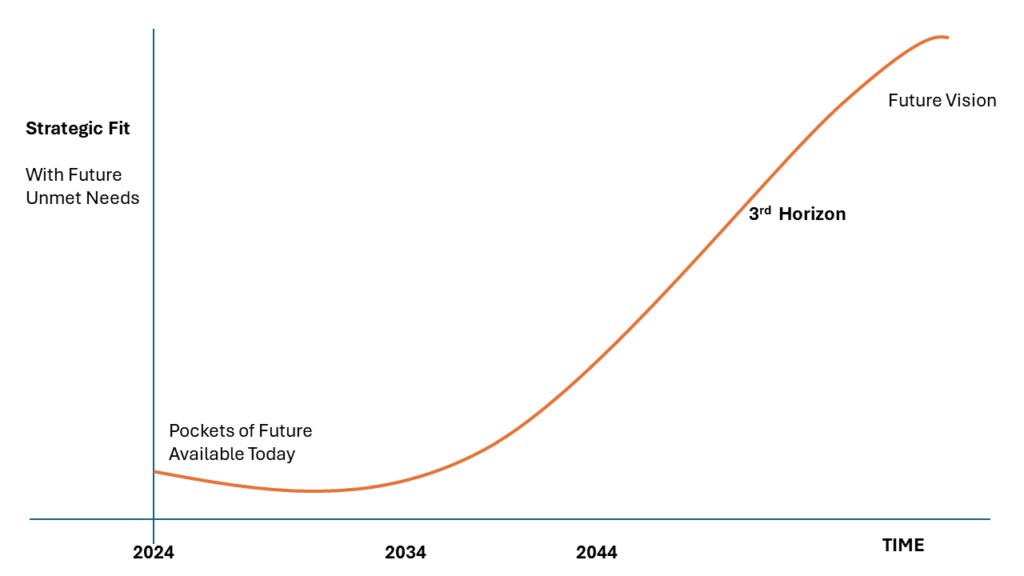
Many companies overlook these disruptors by failing to plan far enough ahead. As an LTSP proponent, you can encourage your team to do more than passively observe these changes. Instead, position your organization to influence and shape these future scenarios.
Horizon 2: Bridging Present and Future
To transition from current offerings to future opportunities, your organization needs a bridge – this is Horizon 2:
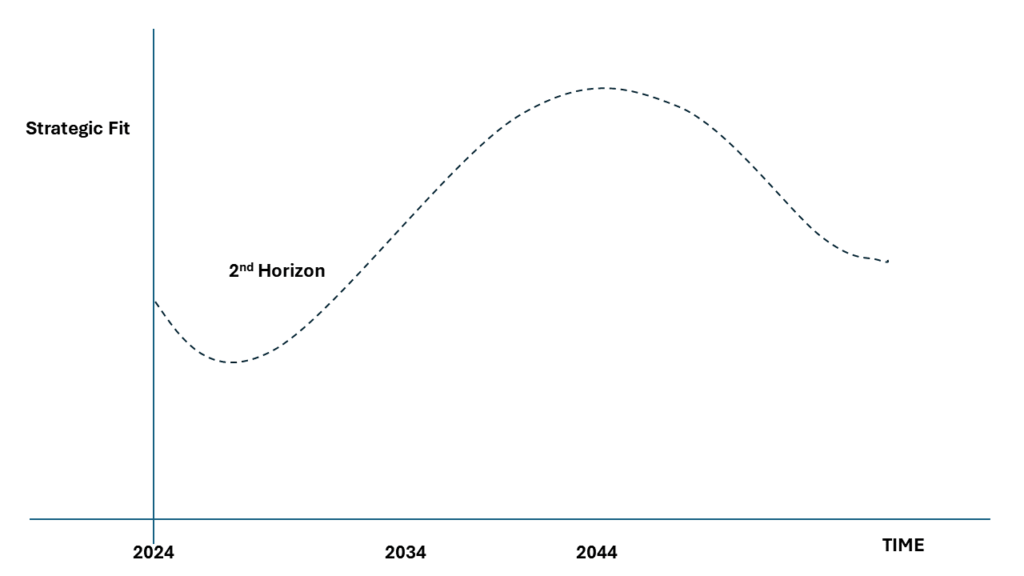
These are initiatives that may not represent your ultimate vision but serve as stepping stones towards it. Developing these transition strategies is best done in strategic planning retreats, where all departments can contribute their insights.
Integrating the Three Horizons
When effectively implemented, the Three Horizons Framework allows your organization to manage current operations, develop transition strategies, and prepare for future scenarios simultaneously:
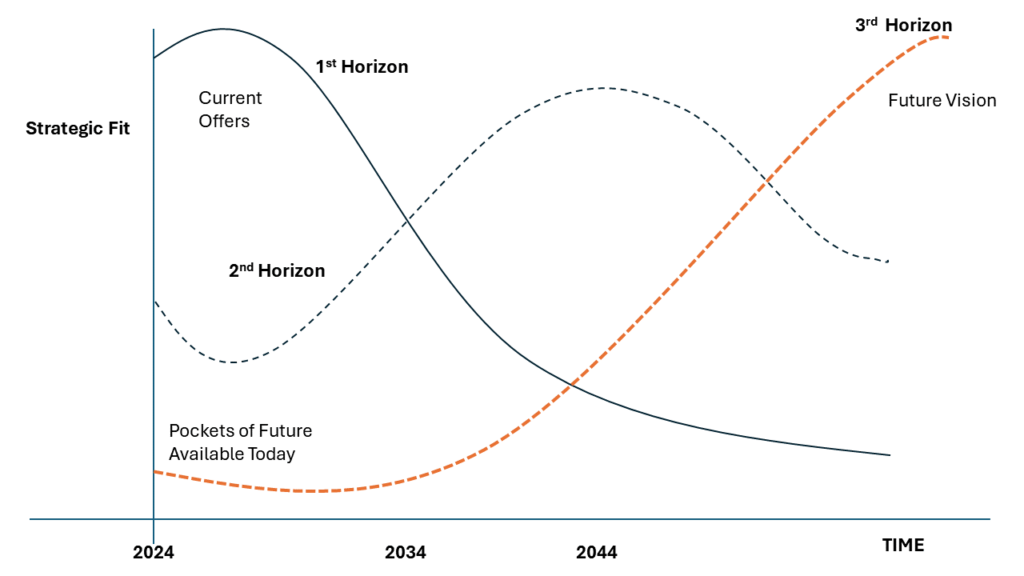
This integrated approach demonstrates how long-term imperatives can and should inform immediate actions.
Conclusion: Empowering Long-Term Strategic Planning
By using the Three Horizons Framework, you now have a powerful tool to illustrate the importance of long-term thinking to your colleagues. This approach allows you to:
1. Visually represent the lifecycle of current offerings
2. Highlight the importance of future-focused initiatives
3. Demonstrate how to bridge present operations with future opportunities
4. Show how all these elements work together in a cohesive strategy
Remember, you’re not alone in advocating for LTSP. Many successful organizations embrace this approach, recognizing that preparation for the future is key to long-term success.
Use this framework to spark meaningful discussions about your company’s future. By doing so, you’re not just planning for tomorrow – you’re shaping it.

